Linux secure programming – LibreSecurity.com
Code repositories
- SVN/GIT repositories
SVN/GIT repositories shall use for any development and testing through whole SDLC.
Only compilable code can be uploaded into repositories.
Branches should merge to main stream after each main version has been tested.
- Ownership of SVN/GIT repositories
Developers shall create branches only rather than main/master repositories.
Only owners of repositories or pre-authorized developers can merge to main/master repositories.
- Comments
Useful comments are a must for each updating.
Meaningless comments are not permitted. e.g. ‘Code optimizing’ ‘New Function’
Code compiling
- Warnings
‘-Wall -Werror’ is a must for any make files.
No warning messages are allowed in repositories.
Higher or beta versions(Higher version) compiler are recommended for development environment.
- Static analysis
Clang static analyst or Pclint are a must for development.
- Dynamic analysis
‘—sanitize=address’ option is a must.
Any other options from Gcc/CLANG sanitizer are recommended.
Valgrind cannot be used as same time with sanitizer.
Readability
- C/C++ pointer conversion
A pointer to one type may be converted to a pointer to another type. The resulting pointer may cause addressing exceptions if the subject pointer does not refer to an object suitably aligned in storage.
Any pointer conversions are not recommended.
<dereferencing type-punned pointer will break strict-aliasing rules [-Wstrict-aliasing]> shall not report by any compiling options.
- Reference of files
No cross reference of files in any projects.
Out of scope reference is not recommended.
- Multi-statement and recursion
Following multi-statement and recursion are not recommended.
if (1)
if(2)
if(3)
if(4)
{
Job();
}
}
}
}
- Returning values
A universal returning values should be defined across any projects.
Multi-return formats should not be used. E.g. ‘return 0, return 1, return -1’ return -1’, all formats shall use ‘return RET_SUCCESS 1, return RET_FAILURE 0, return RET_UNEXPECTED’
- Integer values
Integer values on statement and the call by value method of passing arguments are not recommended. E.g.
while (fgets(buf, 1024, fp) != NULL)
{
memset(tmp, 0, 32);
if (strlen(buf) > 0)
{
sscanf(buf, “%s%32s”, v1, v2);
}
else
{
continue;
}
trim_first_path(v1);
u8 len = 1 + 16 + strlen((const char *) v1);
memcpy(ptr + offset, &len, 1);
offset += 1;
totallen += 1;
trans32_to_16(v2, (u8 *) tmp);
memcpy(ptr + offset, tmp, 16);
offset += 16;
totallen += 16;
memcpy(ptr + offset, v1, strlen((const char *) v1));
offset += strlen((const char *) v1);
totallen += strlen((const char *) v1);
memset(buf, 0, 1024);
memset(v1, 0, 256);
memset(v2, 0, 256);
}
Security
1 Insecure functions
Appendix A
2 Parameters checking
Parameters should be checked in each function call. E.g.
Func1(void *p)
{
Func2(p)
}
Func2(void *p)
{
If(NULL == p)
{
Return -1;
}
//read or write p
}
- Assert
No assert on release version.
- System/getuid functions
Returning values should be checked when these functions are used.
- Root
No root permission for any program, getuid should be used as default.
Performance
- Heap and stack
Using heap only needed. E.g.
Recvpack()
{
Struct sockaddr_in6 *src_addr = NULL;àstruct sockaddr_in6 src_addr;
Src_addr = (struct sockaddr_in6 *)malloc(sock_size);à//DON’T need a heap memory
Memset(&src_addr, 0x0, sizeof(sock_size));
Recvfrom(sock,buffer,len,0,(struct sockaddr *) src_addr,&addr_len);
Recvfrom(sock,buffer,len,0,(struct sockaddr *) &src_addr,&addr_len);
}
- Inline function
Inline functions are recommended for performance sensitive routine. i.e.
While(1)//CPU consuming looping
{
Check_udp_validation();
Get_data_offset();
Handle_registration_msg();
}
For all three functions, inline function is recommended as they are the CPU consuming routine.
- Compiler optimization
Compiler O2 optimization is minimal.
Compiler O3 should be used when it outperformed O2.
Compiler O3 shall be tested for all algorithms.
- Re-entry funtions
High re-entry functions should be optimized according to performance consuming.
| Before | After |
| Recvpack()
{ Recvfrom(*********); Check_udp_validation(##########); If(!can_system_afford()) { Return -1; } Inline_parse(); }
|
Recvpack()
{ If(!can_system_afford()) { Return -1; } Recvfrom(*********); Check_udp_validation(##########); Inline_parse(); }
|
- System calls
All system calls should be checked by strance -c.
All system calls should be counted as necessary.
i.e. the sample process are called unnecessary usleep (nanosleep want wait system calls) and caused CPU waste.
[root@localhost samplet]# strace -c ./bin/sample
Process 7684 detached
% time seconds usecs/call calls errors syscall
—— ———– ———– ——— ——— —————-
77.69 0.107985 14 7715 nanosleep
18.00 0.025016 1668 15 wait4
3.49 0.004857 202 24 clone
0.72 0.001000 167 6 4 ioctl
0.03 0.000041 1 62 sendto
0.03 0.000040 0 1197 3 stat
0.01 0.000016 0 153 mmap
0.01 0.000015 0 51 munmap
0.01 0.000014 0 60 mprotect
0.01 0.000013 0 31 brk
0.00 0.000000 0 125 read
- Perf and profiling
- Programs profiling
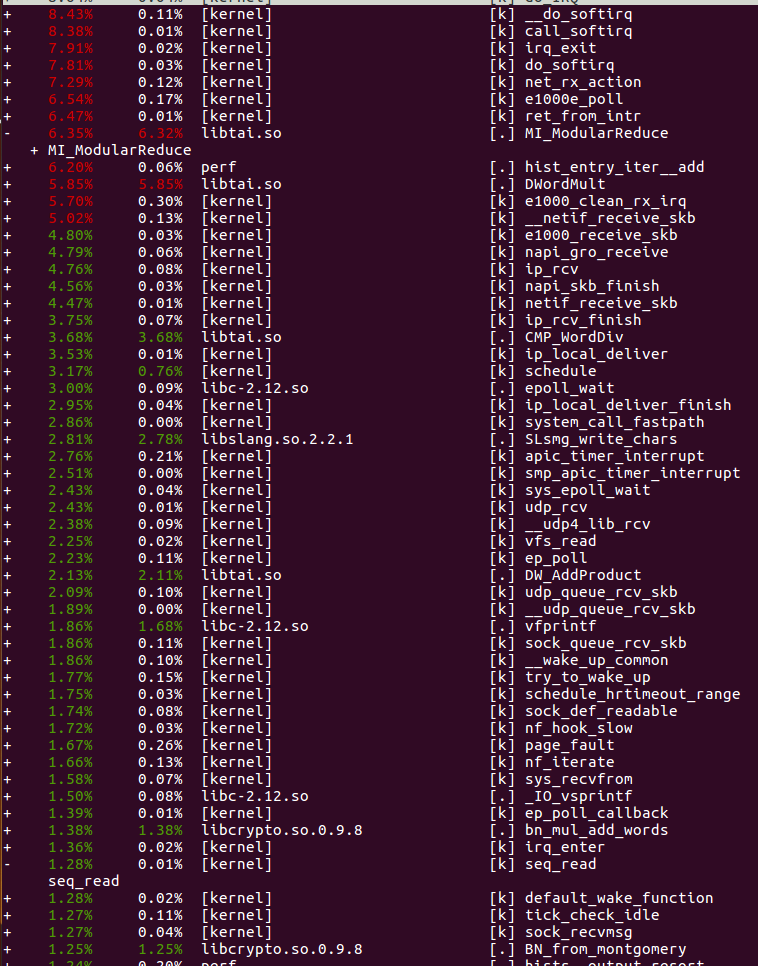
perf record -g <sample> should be used for profiling. i.e. Both mi_modularreduce and wordmult functions consumed CPU timing. This caused by algorithms ORX operationsand libtai.so should be optimized.
2)System profiling
Perf top should be used for system profiling(perf top -g).
All kernel level consuming should be analyzed according kernel CPU timing.
Appendix A Clang static anlyzer
For single file:
clang-3.5 –analyze -Xanalyzer -analyzer-output=html *.c/*.cpp
For project:
1 clang-3.5 –analyze -Xanalyzer -analyzer-output=html your-code-directory/*.c -I your-include-directory/
2 Clang scan-build and scan-view
(1)Using configure generate makefile
1,scan-build-3.5 ./configure
2,scan-build-3.5 make
3,scan-view-3.5 /tmp/xxxxxxxxxx.html
(2)For existing makefile projects
a)scan-build-3.5 make
/usr/share/clang/scan-build-3.5/ccc-analyzer. i.e.
~/code/librebench-1.14$ scan-build-3.5 make
scan-build: Using ‘/usr/lib/llvm-3.5/bin/clang’ for static analysis
make -C src
make[1]: Entering directory `/home/libre/code/librebench-1.14/src’
/usr/share/clang/scan-build-3.5/ccc-analyzer -O2 -c -o xxx.o xxxx.c
scan-view-3.5 /tmp/xxxxxxxxx
b)Manually use makefile
1,Updating compiler through makefile compiler = gcc/cc/armcc/mipscc to compiler = /usr/share/clang/scan-build-3.5/ccc-analyzer
2,scan-build-3.5 makefile
3,scan-view-3.5 /tmp/xxxxxxxxx
- Options
All default.
- PDCA Plan-do-check-act
Single file
clang-3.5 –analyze -Xanalyzer -analyzer-output=html *.c
console output:
Report:
| 214 | char cmd[1024] = {0}; |
| 215 | char backname[512] = {0}; |
| 216 | int fsize = 0; |
| 217 | int ret = 0; |
| 218 | |
| 219 | setuid(0); |
| The return value from the call to ‘setuid’ is not checked. If an error occurs in ‘setuid’, the following code may execute with unexpected privileges | |
| 220 | if(newfile == NULL) |
| 221 | { |
| 222 | Debuging(“newfile == NULL”); |
| 223 | return -1; |
| 224 | } |
http://clang-analyzer.llvm.org/scan-build.html#scanbuild_forwindowsusers
Windows users must have Perl installed to use scan-build.
scan-build.bat script allows you to launch scan-build in the same way as it described in the Basic Usage section above. To invoke scan-build from an arbitrary location, add the path to the folder containing scan-build.bat to your PATH environment variable.
If you have unexpected compilation/make problems when running scan-build with MinGW/MSYS the following information may be helpful:
- If getting unexpected “fatal error: no input files” while building with MSYS make from the Windows cmd, try one of these solutions:
- Use MinGW mingw32-make instead of MSYS make and exclude the path to MSYS from PATH to prevent mingw32-make from using MSYS utils. MSYS utils are dependent on the MSYS runtime and they are not intended for being run from the Windows cmd. Specifically, makefile commands with backslashed quotes may be heavily corrupted when passed for execution.
- Run make from the sh shell:
$ scan-build [scan-build options] sh -c “make [make options]”
- If getting “Error : *** target pattern contains no `%'” while using GNU Make 3.81, try to use another version of make.
