All network data bypass
Most of IPsec and OpenVPN create IP tunnels on VPN clients, e.g. Windows PC, Android, IOS. After VPN sessions are created, which means the routing tables on operating system will be modified after a VPN session activated.
On Fig 2, all network traffic will go through VPN interface ‘eth3’, which routing to VPN server inside the organization. If VPN clients are hacked which can cause malicious transmitted to the organization.

Fig 1 Default routing table
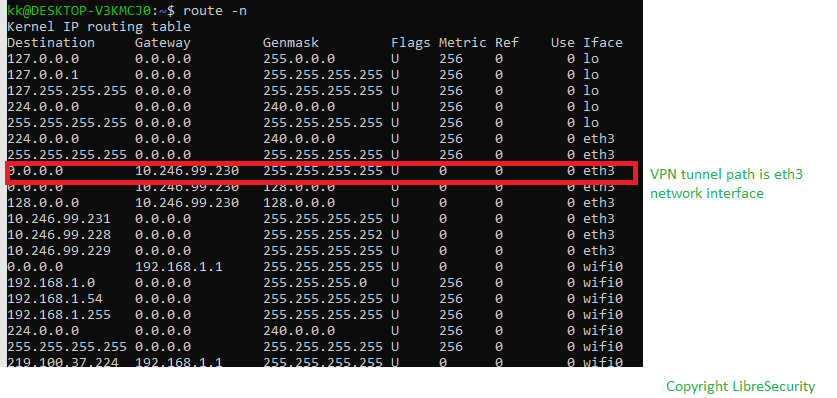
Fig 2 VPN routing table

Fig 3 Data bypass when VPN tunnel activated

Fig 4 VPN traffic inspection
When VPN server enabled traffic inspection or NAC deployed with VPN system, all the VPN clients will be managed and the traffic through VPN tunnel will be filtered by firewall. It may integrated with NAC system to isolate the infected VPN client inside of insecure VLAN.
Black hole or lost connectivity

Fig 5 VPN black hole
PDP (Peer detection protocol) is a protocol to detect VPN peer living when VPN tunnel activated. Most VPN vendors have issues to deliver reliable PDP practice, which caused the common issues of VPN data black hole. VPN users may frustrate by fading PDP protocol, it works intermediately and unable to detect the link status.
Both link detection and tunnel peer detection are recommended to implement which can deliver much reliable PDP status. Also peer re-authentication must be interacted with PDP.
Data filtered by ISP/BGP
Some ISP backbone network system have network traffic filtering device, either by data type filtering or deep traffic inspection. For widely used UDP VPN tunnel traffic will be blocked or blocked intermediately, which can cause VPN connection failure. TCP tunnel and obfuscated traffic must be an alternative protocol implement for sensitive VPN system.

Fig 6 BGP filering
